How Circadian Rhythm Affects Growth and Development
February 2, 2024
WRITTEN BY: POORNA GAYAN WATTALADENIYA, CLASS OF 2024
This blog is about the effects of circadian rhythm on our growth and development and factors that can disrupt and enhance it.
Introduction
Circadian rhythm is the natural cycle of physical, mental, and behavioral changes that occur in a 24-hour period. It is influenced by environmental factors such as light and temperature, as well as internal factors such as hormones and genes. Circadian rhythm regulates many aspects of our physiology, such as sleep, body temperature, metabolism, immune system, and hormone secretion. One of the hormones affected by circadian rhythm is cortisol (stress hormone). Cortisol plays an important role in fetal and infant growth and development, but too much or too little cortisol can have negative impact. In this article, we will explore how circadian rhythm affects growth and development, focusing on the role of cortisol and the growth hormone (GH) axis. We will also discuss some of the factors that can disrupt or enhance circadian rhythm, and some of the strategies that can improve circadian alignment.
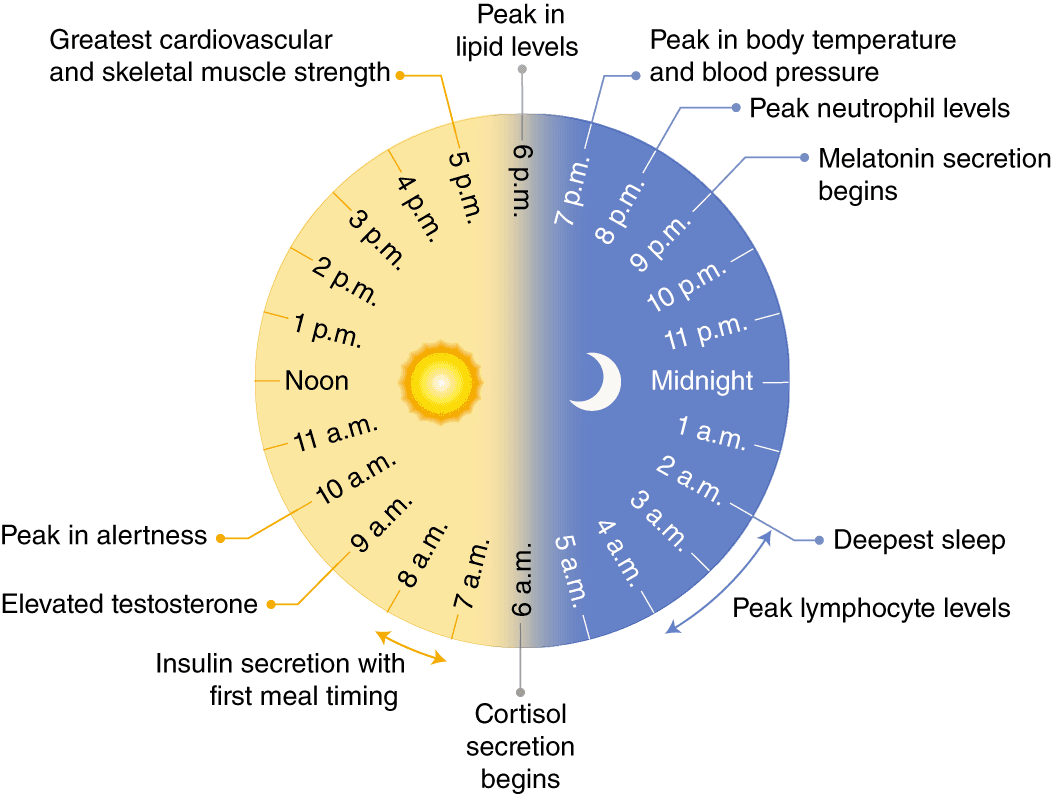
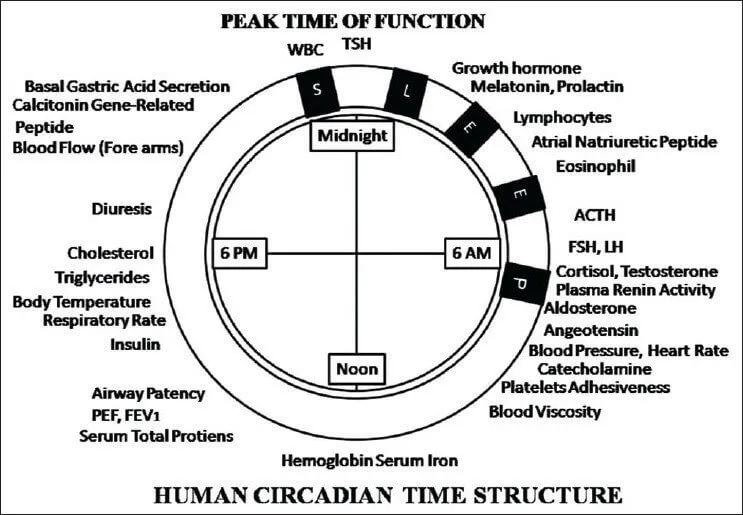
How Cortisol and GH Affect Growth and Development?
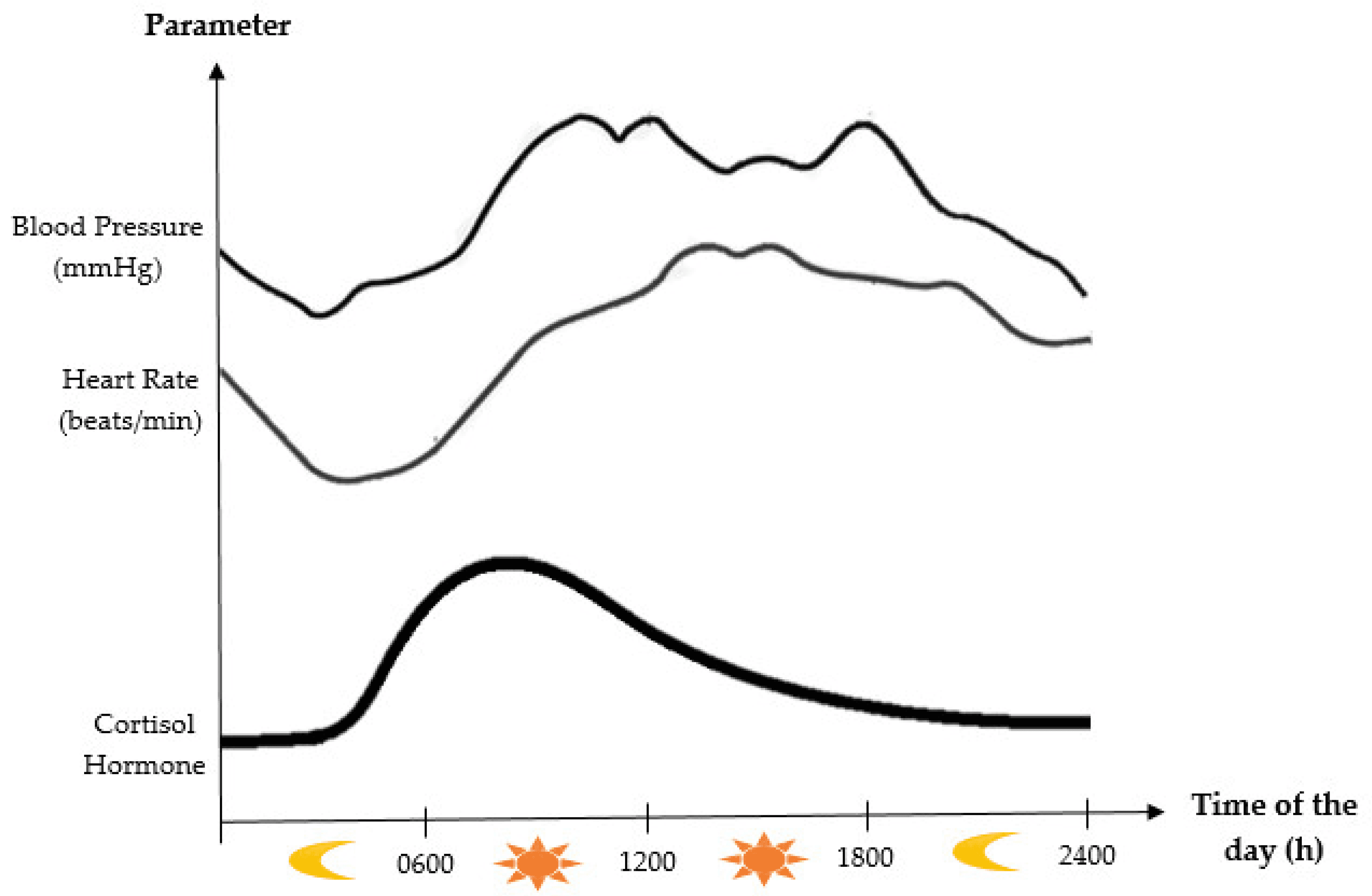
Cortisol is produced by the adrenal glands and helps us cope with stress, inflammation, and infection. However, too much or too little cortisol can have negative impact. Cortisol levels normally follow a circadian pattern, with a peak in the morning and a trough in the evening
It plays an important role in fetal and infant growth and development. It stimulates the maturation of the lungs, liver, kidneys, and other organs in the fetus. It also regulates the growth hormone (GH) axis. GH is secreted by the pituitary gland in a pulsatile manner, with a major peak at night while sleeping.GH stimulates linear growth and body composition by promoting protein synthesis, fat mobilization, and bone formation. GH has anabolic effects on various organs and tissues, such as the brain, heart, liver, and muscles. However, GH secretion is influenced by several factors, including age, sex, nutrition and circadian rhythm. Circadian rhythm is the main factor for GH secretion. It synchronizes GH secretion with the sleep-wake cycle, ensuring that GH is released at the optimal time for growth and repair. Circadian rhythm also regulates the activity of other hormones that modulate GH secretion, such as cortisol, insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), thyroid hormones, and sex steroids.
For example:
Sleep deprivation or poor sleep quality can reduce GH secretion by altering the sleep architecture and reducing the duration of deep sleep.
Jet lag or shift work can disrupt GH secretion by causing a mismatch between the internal clock and the external environment.
Chronic stress or inflammation can increase cortisol levels, which can inhibit GH secretion by interfering with the hypothalamic-pituitary axis
How to Improve Circadian Rhythm for Growth and Development?
To improve circadian rhythm for growth and development, it is important to maintain a healthy balance of cortisol and GH levels. This can be achieved by following some simple tips that can help align your circadian rhythm with the natural light-dark cycle:
• Expose yourself to bright light in the morning and dim light in the evening. This can help reset your internal clock and make you feel more alert during the day and sleepy at night. You can use natural or artificial light to achieve this effect.
• Avoid blue light at night. It is emitted by electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets, computers, and TVs. Blue light can suppress the production of melatonin, which is a hormone that regulates your sleep-wake cycle. Therefore, you should avoid using these devices at least one hour before bedtime or use blue light blocking glasses or apps to reduce their impact.
Maintaining a regular sleep schedule can help your body and mind adjust to a consistent rhythm. This can improve your sleep quality and quantity as well as your mood throughout the day. Sleep for at least seven to nine hours depending on your age and individual needs.
• Avoid caffeine, alcohol and nicotine in the evening. These substances can interfere with your sleep quality and quantity by stimulating your nervous system disrupting your sleep stages or causing you to wake up during the night. You should avoid consuming them at least four to six hours before bedtime or limit them to moderate amounts.
Exercise regularly but not too close to bedtime.
Physical activity can have positive effects on your circadian rhythm by enhancing your alertness during the day and promoting your sleep onset at night.
Moderate exercise in the morning or afternoon can boost your mood and energy levels while avoiding vigorous exercise close to bedtime can prevent sleep disruption.
• Create a comfortable and relaxing sleep environment. Make sure your bedroom is dark, quiet, cool and comfortable by using curtains, blinds, shades, earplugs, fans, white noise machines, thermostat bedding and clothing to suit your preferences.
• Establish a relaxing bedtime routine. Doing some calming activities before bed can help you unwind and prepare for sleep. You can read a book, listen to soothing music or meditate. You should avoid any stressful activities such as work homework or video games.
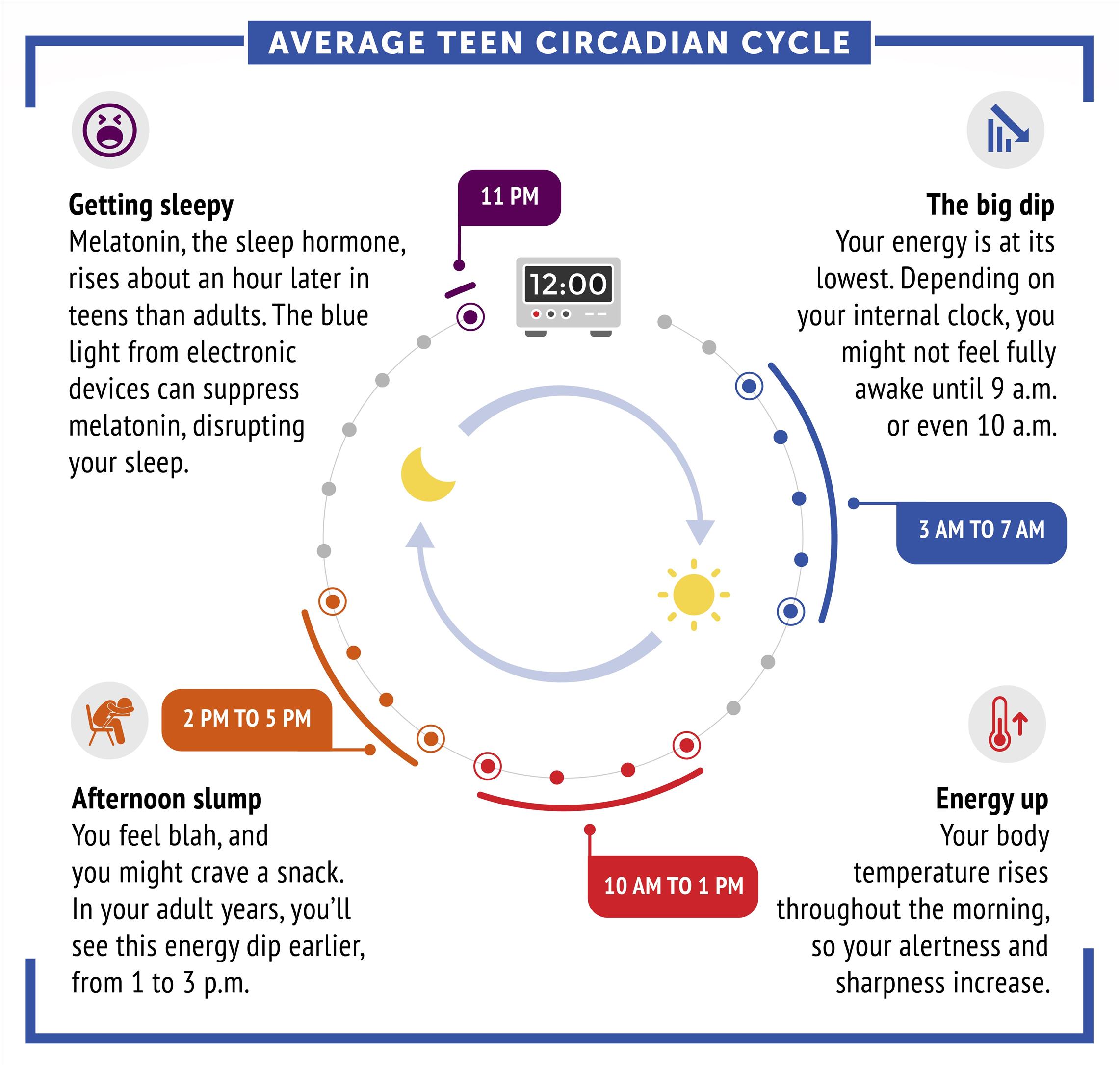
How to measure the Circadian rhythm?
There are several methods to measure your circadian rhythm, which is the natural cycle of physical, mental, and behavioral changes that occur in a 24-hour period. Some of the most common methods are:
• Blood test: A blood test can measure the levels of hormones or molecules that are influenced by circadian rhythm, such as melatonin, cortisol, or body temperature. These levels normally follow a circadian pattern, for example, melatonin is produced more at night than during the day. It reveals the timing and amplitude of these circadian rhythm.
• Actigraphy: It is a method that uses a device called an actigraph, which is worn on the wrist or ankle. The actigraph records the movements and activity of the wearer, which can indicate their sleep-wake cycle and rest-activity cycle. It measures light exposure, which is a major factor that affects circadian rhythm. Its data is analyzed by software.
• Questionnaire: It is a method that uses a self-report survey to assess the preferences and habits of the person regarding their sleep and activity. It also measures the degree of morningness or eveningness. Some examples are, Morningness-Eveningness Questionnaire(MEQ), the Munich Chronotype Questionnaire(MCTQ), or the Horne-Ostberg Questionnaire (HOQ)
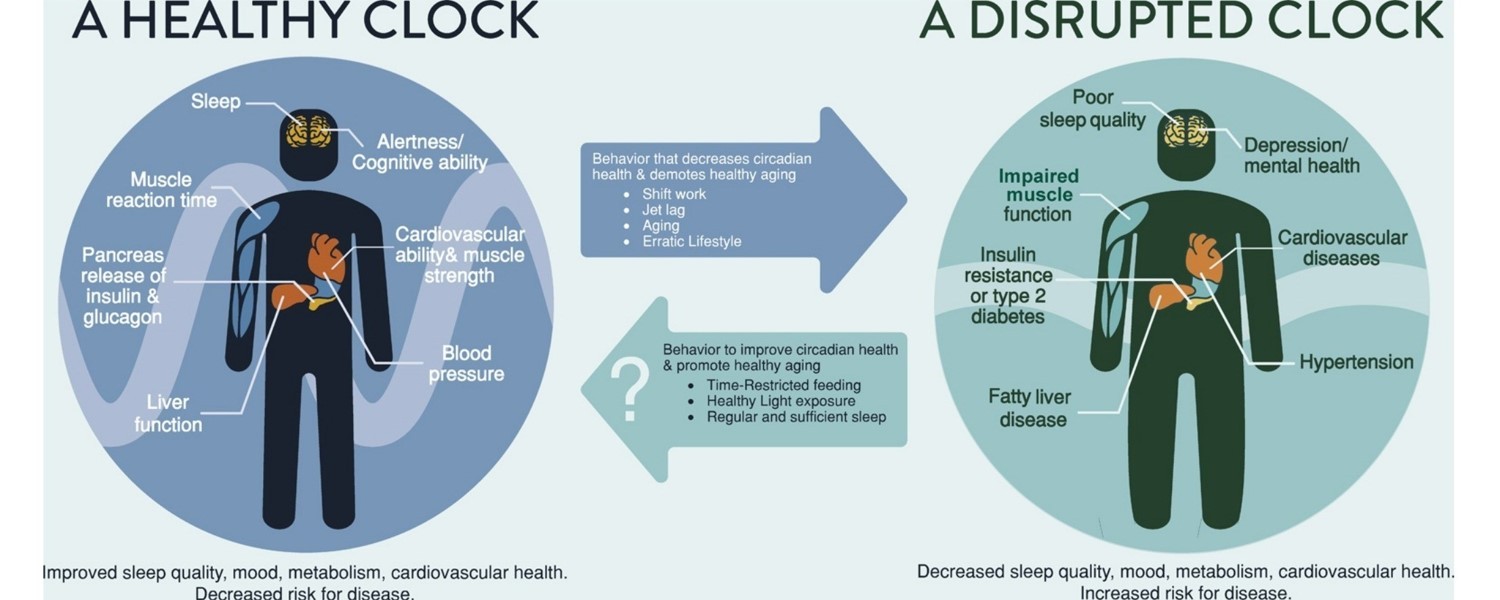
Conclusion
In conclusion, circadian rhythm is a vital factor that affects growth and development by regulating cortisol and GH secretion which support normal growth and maturation of various organs and tissues. However, circadian rhythm can be disrupted by light exposure, feeding schedule, physical and social activities, sleep deprivation, stress or diseases. These can lead to growth retardation or metabolic disorders. Therefore it is important to maintain a healthy circadian rhythm for both mothers and infants.
Here are some tips: expose yourself to bright light in the morning and dim light in the evening; eat regularly, avoid vigorous exercises when about to sleep; avoid social isolation and conflict; adjust to new time zones gradually; get enough sleep quality and quantity; manage stress effectively and seek medical help if needed.