The Ethics Of Gene Editing And Crispr Technology
May 5, 2024
Written By: Krushi Patel, Class of 2024
This blog is about ethical complexities surrounding CRISPR technology and gene editing.
INTRODUCTION
In the realm of biotechnology, few innovations have garnered as much attention and controversy as CRISPR technology. Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats, or CRISPR, is a revolutionary gene-editing tool that allows scientists to modify DNA with unprecedented precision. While its potential for curing genetic diseases and advancing medical science is immense, the ethical implications of gene editing cannot be overlooked. This blog delves into the ethical complexities surrounding CRISPR technology and gene editing.
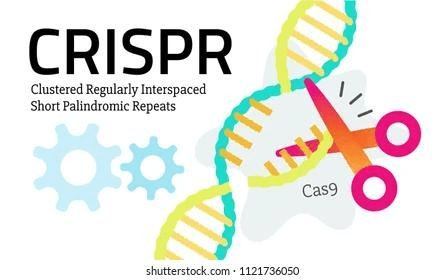
UNDERSTANDING CRISPR TECHNOLOGY
CRISPR is a versatile and powerful tool that allows researchers to precisely alter DNA within living organisms. It works by using a molecule called RNA to guide an enzyme called Cas9 to a specific location in the genome. Cas9 can then cut the DNA at that location, and when the cell repairs the DNA, it may introduce changes, allowing for the addition or removal of specific genetic material.

THE PROMISE OF CRISPR TECHNOLOGY
CRISPR technology has the potential to revolutionize medicine and biology. It can be used to correct genetic mutations responsible for hereditary diseases, opening the door to gene therapy for conditions like cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and muscular dystrophy. It also allows for more efficient drug development, the creation of genetically modified organisms for research and agriculture, and better understanding of the human genome.
THE ETHICAL DILEMMAS
1. Germline Editing: One of the most significant ethical concerns is the modification of germline cells, which would result in changes that are inherited by future generations. This raises questions about the unintended consequences and the potential for designer babies.
2. Consent: Ensuring informed consent is a challenge, especially when it comes to editing the genes of unborn children or those unable to provide consent themselves.
3. Unintended Consequences: Gene editing is not without risks, and the unintended consequences of altering genes could lead to unforeseen health issues. The ethical question here is whether we are justified in experimenting with these risks.
4. Socioeconomic Disparities: Access to gene- editing technology is not equal, potentially exacerbating socioeconomic disparities. This raises concerns about who gets to benefit from this technology.
5. Ethical Boundaries: Where do we draw the line when it comes to editing genes for non-medical purposes, such as enhancing physical or cognitive traits? What's considered an acceptable or unacceptable use of this technology?

REGULATIONS AND OVERSIGHT
The ethical concerns surrounding CRISPR have led to calls for regulations and oversight. Many countries have established guidelines for gene editing, emphasizing the importance of transparent and responsible research. Scientific organizations and institutions are working on developing ethical frameworks to guide the use of CRISPR.
CONCLUSION
CRISPR technology is undoubtedly a ground-breaking scientific achievement with the potential to alleviate human suffering and advance our understanding of genetics. However, it also presents complex ethical challenges that require careful consideration. Striking a balance between innovation and ethical responsibility is crucial. As this technology continues to evolve, open dialogue among scientists, ethicists, policymakers, and the public is essential to ensure that CRISPR is used in ways that benefit humanity while respecting fundamental ethical principles.
